Age can both improve and deteriorate certain health conditions. Sadly, the second group usually includes scoliosis. Scoliosis sufferers must learn how to control their condition as they age, or the consequences could be severe. Even healthy adults should understand how to reduce their risk of developing scoliosis.
What Is Scoliosis
An abnormal curve in the spine, resembling the letters “S” or “C,” is a symptom of the condition scoliosis.” One side of the back may stick out more than the other due to a twist in the spine. Due to the growth of the spine, scoliosis is typically detected in childhood or adolescence.
Various categories, or types, of this spinal disorder, can be distinguished based on the causes of each one as well as their individual symptoms. Common types of scoliosis include:
- Congenital scoliosis – that appears due to birth defects
- Neuromuscular – this type tends to develop due to issues such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy
- Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis – or simply called idiopathic scoliosis, has an unknown cause of onset
- Degenerative scoliosis – appears in adulthood, and is also referred to as late-onset scoliosis, or adult scoliosis
Symptoms
Scoliosis typically has no symptoms. A child’s scoliosis may be discovered during a routine physical examination or a scoliosis checkup at school.
Signs of scoliosis may include:
- Uneven shoulders
- One shoulder blade sticks out farther than the other
- One hip is higher than the other or both hips seem abnormally high
- One breast is higher than the other
- The Head may not be centered directly above the pelvis
- Rib cages are of different heights
- The waist is uneven or there is a skin fold on one side of the waist
- Changes in the appearance of the skin overlying the spine (dimples, hairy patches, color abnormalities)
- The entire body leans to one side
- When symptoms of scoliosis do occur, they may include:
- Back pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Usually when there is a severe curvature
- Scoliosis this severe tends to start in children younger than 10 years
Causes
Some of the most common causes of scoliosis include:
- Birth defects due to incorrect growth of the spine in the womb
- Hereditary factors – some studies suggest that this disorder runs in families, although this affects only a small number of cases of scoliosis patients
- Spinal injuries that may affect the shape of the spinal column
- Aging, as well as degeneration of bone quality over time, may facilitate late-onset scoliosis
Diagnose
Physical examinations are frequently used to identify scoliosis. The Adam’s Forward Bend Test, which is frequently employed in grade school scoliosis screenings, can be used to diagnose scoliosis. The patient leans forward, feet together, and bends 90 degrees at the waist.
From this angle, abnormal spinal curvatures or asymmetry of the trunk can be detected by the examiner. This test can detect potential problems, but cannot determine the exact type or extent of the deformity. Imaging tests used to confirm scoliosis include:
- X-ray
- Spinal radiograph
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- The Cobb Method, which gauges the curve of the spine, is used to determine the severity of scoliosis by counting the number of degrees.
- A curve is considered significant if it is greater than 25 to 30 degrees
- Curves exceeding 45 to 50 degrees are considered severe and tend to require more aggressive treatment
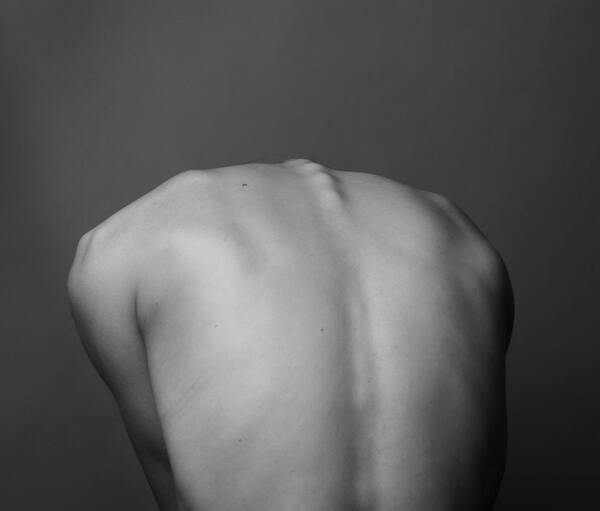
Treatment
The severity of the spinal curvature brought on by scoliosis determines the course of treatment. It may be sufficient to perform particular exercises to reduce the symptoms, especially the pain, of mild forms of scoliosis.
For more severe cases, it might be necessary for the person to wear a brace to support their back and stop the curvature from getting worse.
Adult Scoliosis Prevention
The muscles that support the spine can be strengthened because weakened musculature causes scoliosis. Scoliosis sufferers and those who are at risk for the condition should stay active. Exercises with low impacts, such as yoga and swimming, are frequently the best options.
Degenerative scoliosis can also be caused by conditions that have an impact on bone health, such as osteoporosis. Two of the most important methods for maintaining good bone health are to lose excess weight and consume a diet high in calcium and vitamin D. In order for the spine to rehydrate, it also helps to stop smoking and get at least seven hours of sleep each night.
Scoliosis surgery can be used to treat deformity, but it should only be a last resort. A patient may end up with worse problems as a result of such surgical interventions frequently. As an alternative, you might want to consider using an orthopedic tool to reduce the pain, like the Backrack.
Does Scoliosis Get Worse With Age
Scoliosis has a propensity to get worse over time, especially if it goes untreated. It doesn’t matter what age the condition advances. In other words, it can worsen into adulthood and even old age, not just affecting children and teenagers who are still going through growth spurts.
Numerous variables, including the severity of the abnormal curvature, affect how quickly the disease progresses. The longer this condition is untreated, however, the greater the likelihood that complications will arise and pre-existing symptoms will worsen, including the progression of the curve.